What is Down syndrome?
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder that occurs when a person has an extra partial or full chromosome 21. There are three types of down syndrome including Trisomy 21 (Nondisjuction), Mosaicism Down syndrome, and Translocation Down syndrome. These terms refer to the different errors in cell division that result in an extra chromosome 21. The genetic disorder down syndrome influences the physical, cognitive, and behavioral development of individuals who possess it.
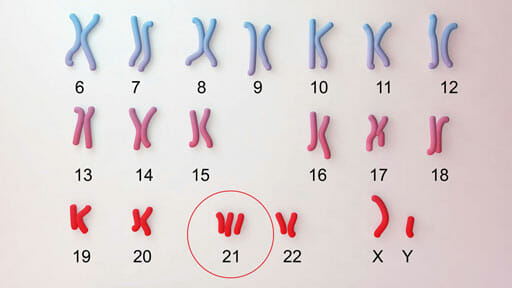
How Common is Down syndrome?
According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, “Each year, about 6,000 babies born in the United States have Down syndrome. This means that down syndrome occurs in about 1 in every 700 babies.” This makes down syndrome the most frequent chromosomal condition diagnosed in the U.S.
What are the Symptoms of Down Syndrome?
The symptoms of down syndrome are not the same in each individual with the condition. However, a commonly seen physical indicator is hypotonia, or decreased muscle tone. Hypotonia can make ordinary or day to day movements more difficult to complete. In addition, it can delay the development of gross and fine motor skills. Other common physical symptoms of down syndrome are a flattened face, upward slanted eyes, and a short neck, but it should be noted that down syndrome does not look like one thing. People who have the condition vary greatly in physical appearance. Along with physical symptoms, down syndrome often impacts cognition and behavior. Down syndrome can cause intellectual disability and delayed milestones in learning, such as in speech. It is important to realize that the symptoms of down
syndrome are not consistent from person to person.
What we see…
Furthermore, it is critical to understand that the expected abilities of individuals with the disorder are not to be limited as they are wide ranging and extensive. Those with down syndrome should be treated as the capable and individually unique people they are, regardless of the extra chromosome they possess.
Written by Ava P’ng (Generation G Youth Board Member)
Sources:
● National Down Syndrome Society “About Down Syndrome”
https://ndss.org/about
● Center for Disease Control and Prevention “Down Syndrome”
https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/downsyndrome.html
● Kids Health “Down Syndrome”
https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/down-syndrome.html
● Penn Medicine “Down syndrome”
https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treat
ed-a-to-z/down-syndrome
● Healthline “What is Hypotonia?”
https://www.healthline.com/health/hypotonia#causes
● Photo: National Humane Genome Research Institute “About Down
Syndrome”
Recent Posts



